HemEx™-TypeH
Human HSC expansion basal medium
Product Basics
HemEx™-TypeH (human HSC expansion basal medium) is specially formulated for the expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). Based on Iscove’s MDM, it can expand long-term HSCs (LT-HSCs) from umbilical cord blood-derived (CB) hHSCs and peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs). This product contains only Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium-Ethanolamine (ITS-X) as a supplement, allowing users the flexibility to combine cytokines and small molecules.
Contaminants derived from albumin can trigger the differentiation of HSC. By replacing albumin with polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer (PCL-PVAc-PEG, Soluplus), HemEx-TypeH can maintain HSCs in an undifferentiated state for over one month of expansion culture.
Key Features
- Serum free. Albumin free
- Chemically defined
- Verified proliferation of human HSC and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC)*
- Development was supervised by Dr. Satoshi Yamazaki (Tokyo University, Japan)
*Requires the addition of cytokines
Key Applications
- Expansion of LT-HSCs from umbilical cord blood-derived (CB) hHSCs ¹
- Expansion peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) ³
- Flow cytometric analysis can be performed on cultured HSCs at any stage
- Suitable for in vivo transplantation assays
Technical Information
Flexible Design
HemEx™-TypeH contains only Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium-Ethanolamine (ITS-X) supplement, enabling flexible addition of cytokines and small molecules.
HemEx™-TypeH is free of antibiotics, additional cytokines, activators, and inhibitors, and it is necessary to add L-glutamine (4mM).
Recommended supplements to complete HemEx™-TypeH base medium
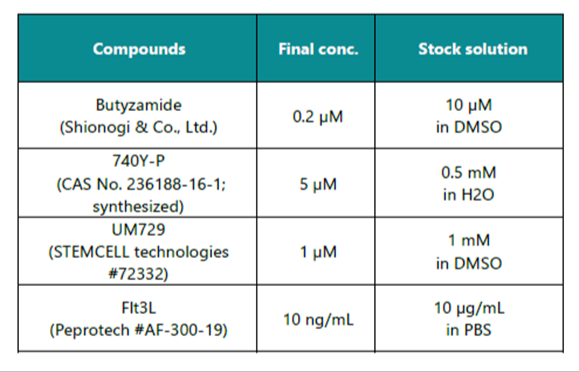
Example of Tailored Application: Adding 2 μM bortezomib, 1 μM lenalidomide, and 100 ng/mL TRAIL in complete medium (HemEx™-TypeH + recommended supplements) for myeloma cell purging in PBSC cultures.³
Maintaining the Undifferentiated State
HemEx™ -TypeH utilizes PCL-PVAc-PEG instead of albumin to suppress the differentiation of HSCs.
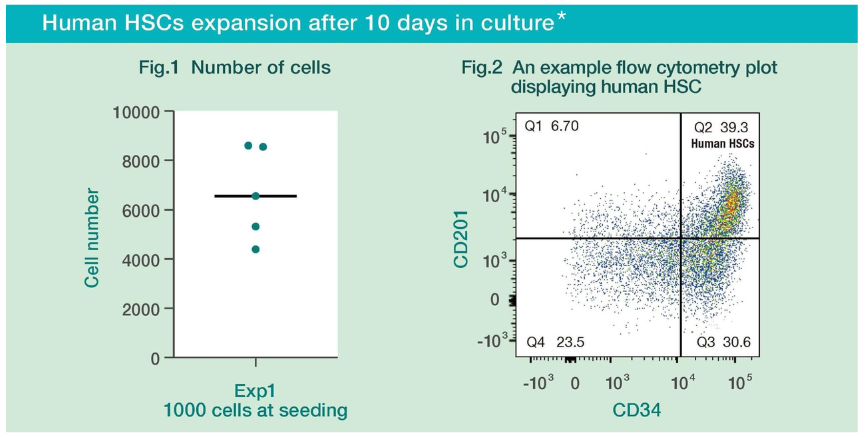
Human HSCs expansion after 10 days in complete HemEx™ -TypeH.¹
Fig.1 Umbilical cord blood-derived (CB) hHSCs cultured with HemEx™ -TypeH proliferated well for 10 days.
Fig.2 When the cultured human HSC cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, it was confirmed that the characteristics of human HSC were maintained.¹
*Requires the addition of cytokines
Rapid expansion of human HSCs cultured in HemEx™-TypeH
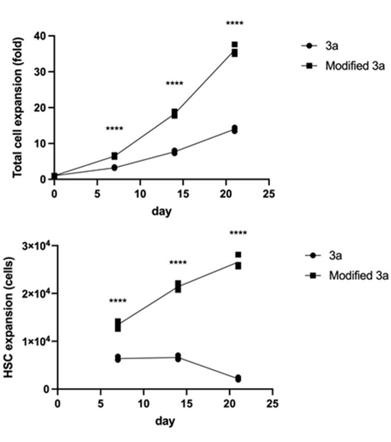
Fig. 3 HemEx™-TypeH (Modified 3a) achieved rapid 35-40-fold expansion of HSC (CD34+CD45RA−CD90+EPCR+ITGA3+ cells) by day 21.
Ishitsuka et al. Experimental Hematology 2024. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2023.104138 CC BY 4.0 /Cropped from original
More Phenotype HSCs: Comparison of HSC expansion in HemEx™-TypeH and Other Culture Conditions
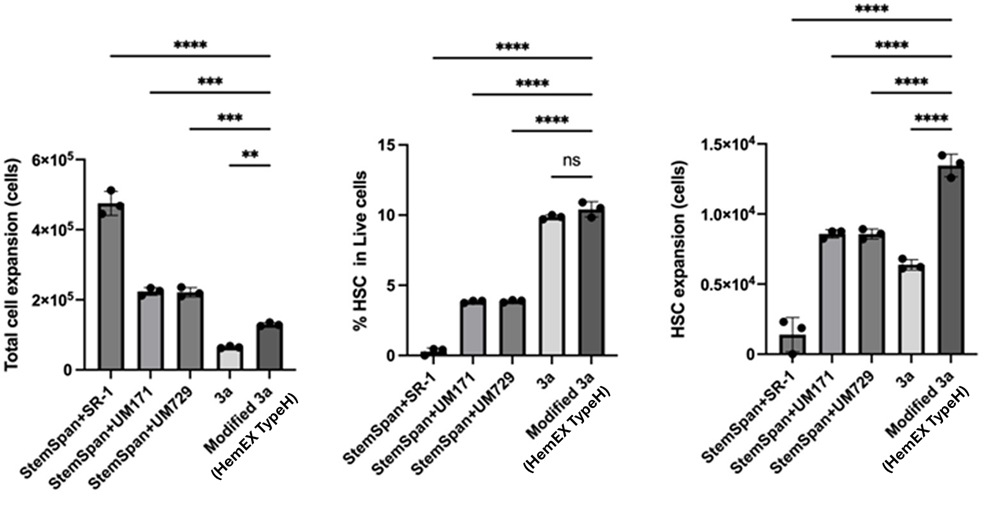
Ishitsuka et al. Experimental Hematology 2024 doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2023.104138 CC BY 4.0 /modified X-axis label
Fig. 4
Expansion efficiency of the modified-3a medium (HemEx™-TypeH) was compared with standard 3a* and StemSpan™ SFEM-based media supplemented with UM171, UM729, or SR-1. After 7 days of cord blood CD34⁺ cell culture, total cell numbers were higher in StemSpan-based media. However, the number and proportion of phenotypic HSCs (CD34⁺CD45RA⁻CD90⁺EPCR⁺ITGA3⁺) were increased in the modified-3a medium (HemEx™-TypeH).³
*3a = UM171, 740Y-P, and butyzamide
Specification
- Size: 100mL
- Storage temperature: 4°C
- Shelf life: To be determined
- Manufactured by: Cell Science and Technology Institute
Pricing
References
- Sakurai, M. et al. Chemically defined cytokine-free expansion of human haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 615, 127–133 (2023) doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05739-9.
- Sakurai, M., Ishitsuka, K. & Yamazaki, S. Chemically defined cytokine-free expansion of human haematopoietic stem cells. Protocol Exchange (2023) doi: 10.21203/rs.3.pex-2163/v1.
- Ishitsuka, K., Nishikii, H., Kimura, T., Sugiyama-Finnis, A. & Yamazaki, S. Purging myeloma cell contaminants and simultaneous expansion of peripheral blood-mobilized stem cells. Experimental Hematology 131, 104138 (2024) doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2023.104138. Licensed under CC BY 4.0
Other Documents
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES